AWS Solution Architect Associate - CheatSheet
Intro
Exam Code: SAA-C03
Glossary
Storage/Data Tier - Level of access
- Hot Storage
- Access Speed: Fastest, optimized for frequently accessed data.
- Cost: Most expensive due to performance optimization.
- Use Cases: High-performance computing, real-time analytics, frequently accessed applications.
- Warm Storage:
- Access Speed: Slower than hot storage, but still relatively quick.
- Cost: Less expensive than hot storage.
- Use Cases: Data used for reporting, analytics, or data that needs to be accessed occasionally but not frequently.
- Cold Storage:
- Access Speed: Slowest, with potential delays for retrieval.
- Cost: Least expensive.
- Use Cases: Archiving, long-term data retention, infrequently accessed data.
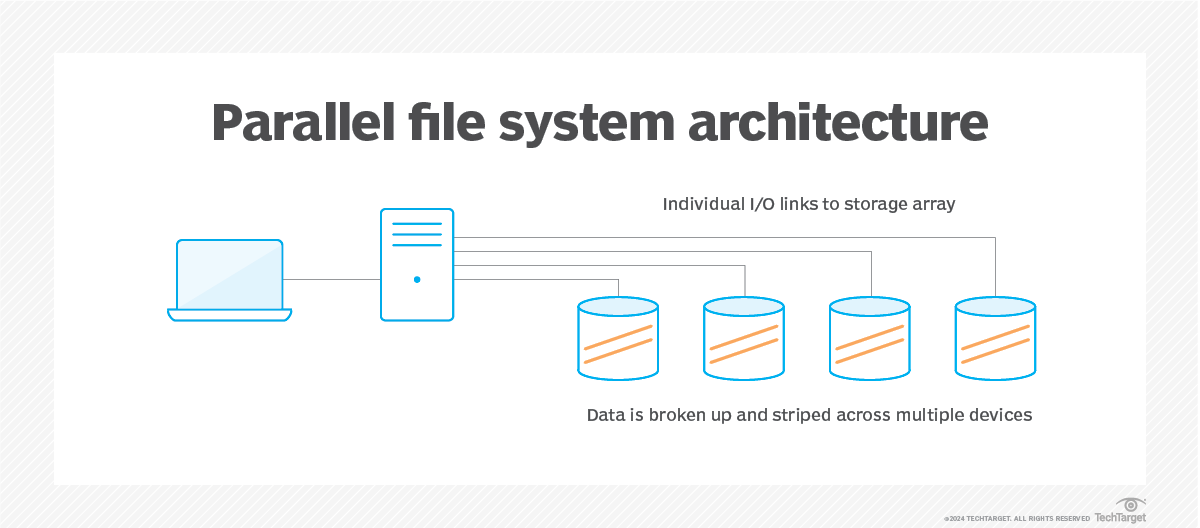
Parallel file system:
- Is a software component designed to store data across multiple networked servers. It facilitates high-performance access through simultaneous, coordinated input/output (I/O) operations between clients and storage nodes.
- Parallel file system can span thousands of server nodes and manage petabytes of data. Users typically deploy high-speed networking, such as Fast Ethernet, InfiniBand and proprietary technologies, to optimize the I/O path and enable greater bandwidth.
Serverless:
- A cloud-native development model that allows to run applications without having to manage servers.
- It doesn’t mean there are no servers, it means the servers are abstracted away from application development. A cloud provider handles the routine work of provisioning, maintaining, and scaling the server infrastructure.
- Serverless apps respond to demand and automatically scale up or down as needed. When a serverless function is sitting idle, it doesn’t cost anything.
Reference:
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchstorage/definition/parallel-file-system
- https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/cloud-native-apps/what-is-serverless
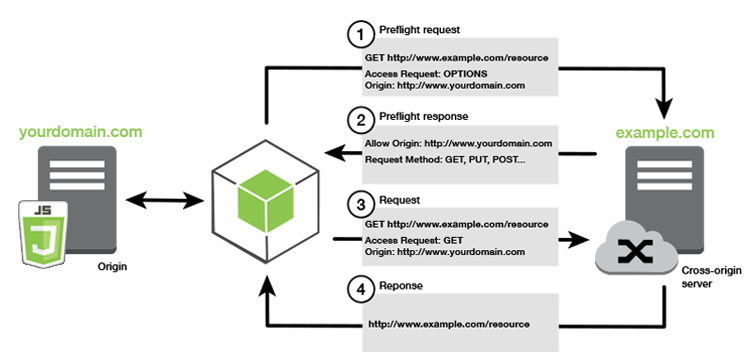
Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) defines a way for client web applications that are loaded in one domain to interact with resources in a different domain. With CORS support, you can build rich client-side web applications with Amazon S3 and selectively allow cross-origin access to your Amazon S3 resources.
High-cardinality (In database term) refers to columns with values that are unique. High-cardinality column values are typically ID number, email, user name or the combination of these. In general definition, “High-cardinality” means the characteristic of multiple possible unique value of an object. There are many problem handling high-cardinality data structure like IOT scenario, database partitioning, …
Read more: https://khangtictoc.github.io/posts/storage-data-consistency-and-partition/
Common Architecture
1. Fan-out Pattern
The fan-out pattern is a messaging or workload distribution pattern where a single message or task is sent to multiple downstream consumers or workers for parallel processing. It enhances scalability and decouples producers from consumers.
How it Works
- A producer sends a message to a central messaging system (e.g., a queue or topic).
- The messaging system distributes (“fans out”) the message to multiple consumers.
- Each consumer processes the message independently, often in parallel.
AWS Example
In AWS, the fan-out pattern is commonly implemented using Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service) and SQS (Simple Queue Service):
- Scenario: An e-commerce platform processes an order by notifying services like inventory management, payment processing, and shipping.
- Implementation:
- An application publishes an order event to an SNS topic.
- The SNS topic fans out the message to multiple SQS queues (e.g.,
InventoryQueue,PaymentQueue,ShippingQueue). - Each queue is processed by a service, such as a Lambda function or EC2 instance.
- AWS Services:
- SNS + SQS: SNS topic fans out to SQS queues, processed by Lambda or other services.
- Kinesis Data Streams: A stream fans out to multiple consumers (e.g., Lambda functions).
- EventBridge: An event bus distributes events to multiple targets (e.g., Lambda, ECS).
- Benefits:
- Scalability: Independent scaling of consumers.
- Decoupling: Producer is unaware of consumer details.
- Parallel Processing: Multiple services handle the same event concurrently.
- Use Case: A video processing application uploads a video to S3, triggering an SNS topic that fans out to SQS queues for thumbnail generation, transcoding, and metadata extraction.
2. Blue-Green Deployment
Blue-green deployment is a release strategy that reduces downtime and risk by maintaining two identical environments: one active (blue) and one idle (green). The new version is deployed to the green environment, tested, and then traffic is switched from blue to green.
How it Works
- Blue Environment: Current production environment serving live traffic.
- Green Environment: New environment with the updated application, initially idle.
- Traffic is switched from blue to green (e.g., via DNS or load balancer) after testing.
- The blue environment remains available for rollback if issues arise.
AWS Example
- Implementation:
- Use AWS Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) with Auto Scaling Groups (ASGs).
- Blue: ASG with the current version behind ELB.
- Green: ASG with the new version behind the same ELB.
- Use AWS CodeDeploy to switch traffic from blue to green.
- Benefits:
- Zero downtime with instant traffic switching.
- Easy rollback to the blue environment.
- Full testing in the green environment before going live.
- Challenges:
- Duplicated infrastructure increases costs.
- Database migrations require careful handling.
- Use Case: Deploying a new version of an SAP HANA-integrated application on EC2, using CodeDeploy to switch traffic between ASGs.
3. Canary Deployment
Canary deployment is a release strategy where a new version is rolled out to a small subset of users for testing before a full deployment. It minimizes risk by validating the new version in production.
How it Works
- The new version (canary) runs alongside the stable version.
- A small percentage of traffic (e.g., 5%) is routed to the canary version.
- Monitoring tools check the canary’s performance (e.g., errors, latency).
- Traffic is gradually shifted to the canary if it performs well, or rolled back if it fails.
AWS Example
- Implementation:
- Use AWS Application Load Balancer (ALB) with weighted target groups.
- Stable: Target group A (95% traffic).
- Canary: Target group B (5% traffic).
- Use AWS CodeDeploy or ALB rules to shift traffic incrementally.
- Monitor with Amazon CloudWatch.
- Benefits:
- Low risk: Issues affect only a small user base.
- Real-world testing with actual traffic.
- Granular control over traffic distribution.
- Challenges:
- Requires advanced routing and monitoring.
- Session persistence may be needed.
- Use Case: Rolling out a new feature for a web application, using ALB to route 10% of traffic to the canary version with CloudWatch monitoring.
Comparison & Differences
Storage
Storage use cases & solutions
| Name | Services |
|---|---|
| Object Storage |
|
| File Storage |
|
| Block Storage |
|
| Data Transfer |
|
| Backup |
|
Typical storage services & its feature
| Services | Features | Parallel system, process concurrent task ? | POSIX-compliant file system ? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon FSx For Lustre |
| Yes | Yes |
| Amazon FSx for Windows File Server |
| No | No |
| Amazon Elastic File System |
| Yes | Yes |
Computing
Overview comparison
| Service | Serverless? | Burst Capability |
|---|---|---|
| EC2 | No | Handle the bursts of traffic in minutes |
| ECS | No | Handle the bursts of traffic in minutes |
| Lambda | No | Handle the bursts of traffic in seconds |
Distinguish
Streaming vs Queue services
| Concept | Streaming Service (e.g., Kinesis, Kafka) | Queue (e.g., SQS) |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Log-based stream (publish-subscribe model) | Message queue (point-to-point model) |
| Message delivery | Multiple consumers can independently read the same data | Message is processed once |
| Retention | Messages kept for fixed window (e.g., 24h–7d+) | Message deleted after being consumed |
| Ordering | Strong ordering (per shard/partition) | FIFO queues support ordering |
| Replaying | ✅ Yes – consumers can re-read from earlier point | ❌ No – message is gone after deletion |
| Use cases | Real-time analytics, stream processing, ETL | Task queues, decoupling services |
| Scale | High throughput & parallelism per partition | Simpler to scale horizontally |
| Latency | Low latency | Slightly higher due to polling |
| Service | Kafka, Amazon Kinesis | **Amazon SQS, RabbitMQ |
NOTE:
- Amazon MQ is primarily used as a managed message broker service and not a queue
Differents in Streaming/Queue services
| Concept | Feature | Use Case/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon MQ | ||
| AppStream | ||
| Data Firehose | Process data stream | Integrate with another services like Lambda or similar ones to process data then bring those data for further action consumption |
| Kinesis Data Stream | Consume data stream | Consume data in a stream for downstream tasks like analytics, query, … |
Differents in “Interface” and “Gateway” VPC endpoint
| Interface | Gateway | |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Pay an hourly rate for every provisioned Interface endpoint | Free |
| Supported services | Most of services | Only Amazon S3 & DynamoDB |
Service Summary
Compute
EC2
Storage/Disk
Instance Store volume: a temporary block-level storage for EC2 instances
Monitoring
Default metrics:
- CPU
- Network/Bandwidth, Read/Write bytes
Not-ready metrics:
- Memory, Disk I/O:
- Memory utilization
- Disk swap utilization
- Disk space utilization
- Page file utilization
- Log collection
Install metrics:
- Memory, Disk I/O: Install the Amazon CloudWatch agent to all the EC2 instances. View the custom metrics in the CloudWatch console.
Dynamic scaling policy
Types: Simple scaling
- Based on CloudWatch alarm.
- Choose 1 action to conduct.
- Scale-in operation depends on CloudWatch alarm.
Target tracking policy
- Based on CloudWatch & built-in metrics (i.e Averge CPU Utilization). CloudWatch metrics must be available or defined.
- Scale (in/out) operations trigger by calculating the current resources utilization that matches the defined target metric.
- Faster scale-in operation.
Step scaling
- It is a
Simple scalingwith various actions. - Apply multiple actions for a scaling events.
- Allow scaling operation more smoothly and optimized.
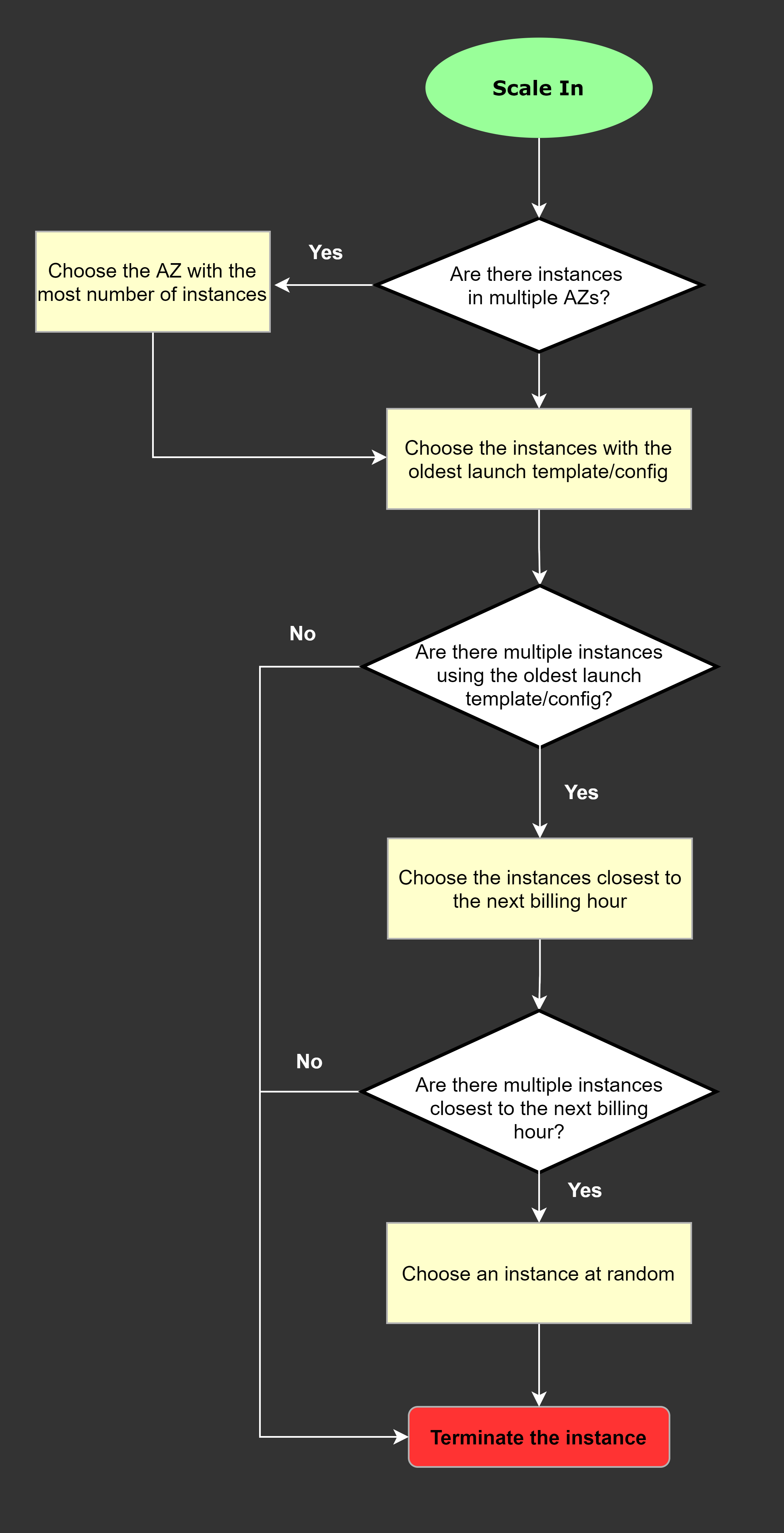
Scale-In Mechanism
Auto Scaling services choose below critiria to perform terminate EC2 instances
Priority:
- AZ has the most VMs
- Oldest launch templates (lowest version)
- Closet to next billing hour
- RANDOM if can’t decide more.
Operation
Take snapshot & restore
Annotations:
- Source instance to take snapshot:
instance A - Destinated instance to perform restore:
instance B
Steps:
- Take snapshot of a running
instance A’s volumes. We havesnapshot A - Create a new volume from
snapshot A. We havevolume A - On the target
instance B, shutdown the instance. - Force detachment on the
volume Bofinstance B. Then delete the volume if not use anymore - Attach the new
volume Atoinstance B. - Start
instance B. - Verify the
instance Bwith new snapshotsnapshot A
Restart instance
Notes:
- Only EBS-backed instances can be stopped and restarted
- Store-backed instance can only be rebooted or terminated, and its data will be erased if the EC2 instance is either stopped or terminated.
Keep-in-mind:
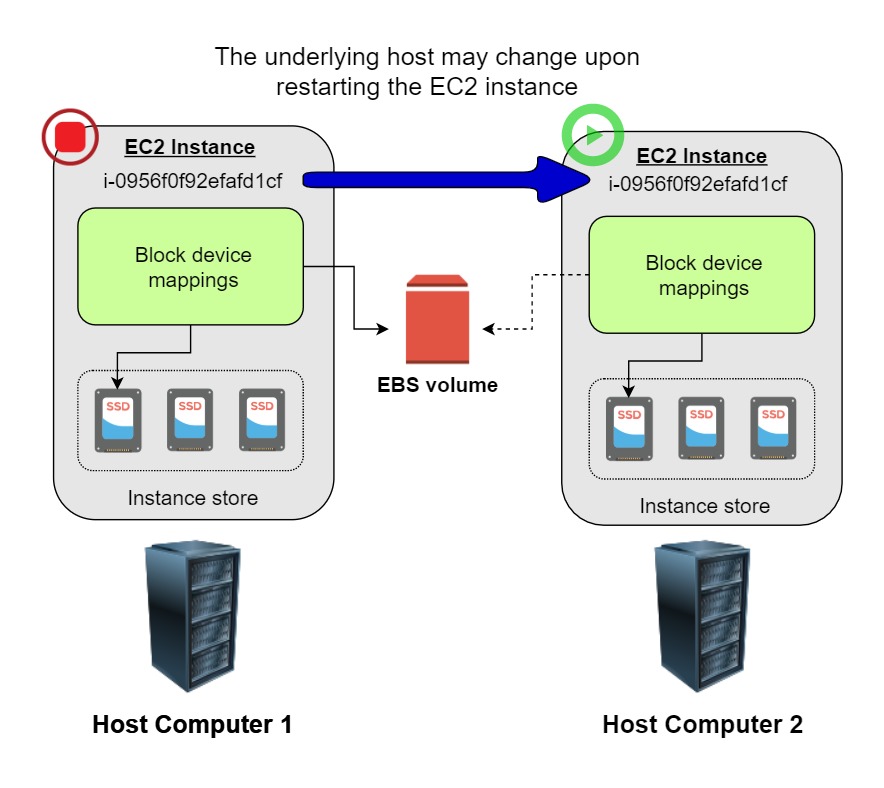
- When stopping an EBS-backed EC2 instance, the volume is preserved, but the data in any attached instance store volume will be erased.
- An EC2 instance has an underlying physical host computer. If the instance is stopped, AWS usually moves the instance to a new host computer.
- Your instance may stay on the same host computer if there are no problems with the host computer.
- In addition, its Elastic IP address is disassociated from the instance if it is an EC2-Classic instance. Otherwise, if it is an EC2-VPC instance, the Elastic IP address remains associated.
Stop Reserved instances
- Go to the AWS Reserved Instance Marketplace and sell the Reserved instances.
- Terminate the Reserved instances as soon as possible to avoid getting billed at the on-demand price when it expires.
Reference: EC2 instance Stop/Start
Load Balancer
Application Load Balancer
Main features
- Layer-7 OSI load balancer
- Can not assign Elastic IP
Configurations
- Hibernation Mode: It is not possible to enable or disable for an instance after it has been launched -> Migrate to an EC2 instance with hibernation enabled.
Network Load Balancer
- Layer-4 OSI load balancer
- Can assign Elastic IP
Billing
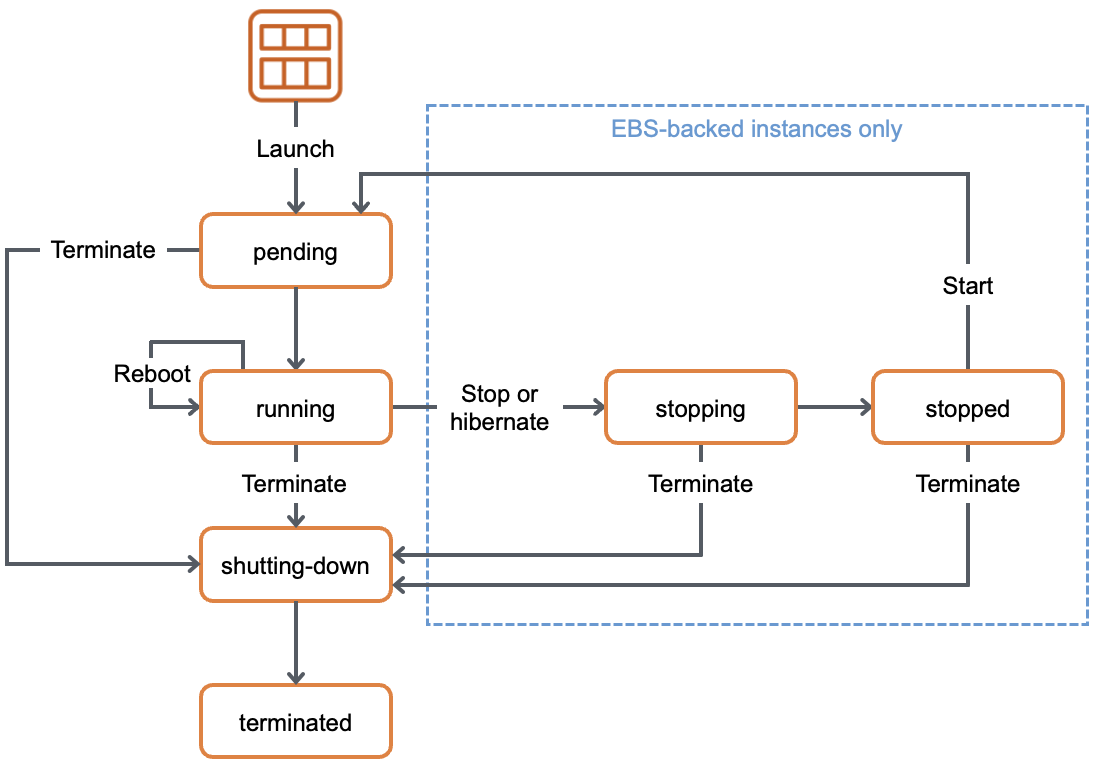
Instance state lifecycle
Below are the valid EC2 lifecycle instance states:
| Instance state | Description | Instance usage billing |
|---|---|---|
| pending | The instance is preparing to enter the running state. An instance enters the pending state when it is launched or when it is started after being in the stopped state. | Not billed |
| running | The instance is running and ready for use. | Billed |
| stopping | The instance is preparing to be stopped. Note: If you hibernate an instance, you’re billed while the instance is in the stopping state. | Not billed |
| stopped | The instance is shut down and cannot be used. The instance can be started at any time. | Not billed |
| shutting-down | The instance is preparing to be terminated. | Not billed |
| terminated | The instance has been permanently deleted and cannot be started. Note: Reserved Instances that applied to terminated instances are billed until the end of their term according to their payment option. | Not billed |
Reference: Instance state lifecycle
Analytics
AWS Glue
Main features
- Enables data engineers to build and manage ETL(extract, transform, load) pipelines for processing and analyzing large amounts of data
Configurations
- Job Bookmarking: A mechanism that allows AWS Glue to keep track of where a job is left off in case it gets interrupted or fails for any reason. This way, when the job is restarted, it can pick up from where it left off instead of starting from scratch.
Application Integration
Simple Queue Service (SQS)
Main features
- Create a queue of messages
- Expose an endpoint and wait for other applications to consume
- Producer/Consumer architecture
NOTE: Can be combined with SNS to create Fan-out architecture.
Simple Notification Service (SNS)
Main features
- Create a queue of messages, stored in Topic
- A service or application will register (subscribe) a Topic.
- Whenever a message is pushed (publish) in a SNS Topic, immediately push to a subscribed endpoint
- Pub/Sub architecture
NOTE: Can be combined with SQS to create Fan-out architecture.
Containers
Elastic Kubernetes Service
Configuration
- Secret encryption (On/Off): with a AWS KMS -> Encrypt sensitive data stored in etcd
Database
DynamoDB
Main features
- NoSQL database
Configuration
DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX) used to significantly improve the in-memory read performance of your database
A DynamoDB stream is an ordered flow of information about changes to items in an Amazon DynamoDB table. When you enable a stream on a table, DynamoDB captures information about every modification to data items in the table to process further tasks
Amazon Kinesis Client Library (KCL) is a coding module to write an application that leverages on DynamoDB Streams Kinesis Adapter that will fetch data from the DynamoDB Streams endpoint.
Point-in-Time Recovery (PITR) is a backup features:
- Take snapshot at any point of time
- Store short-term snapshots
- Optimized solution for RPO/RTO metric.
Redshift
Main features
- Data warehousing solution
- Built on a relational database model
RDS
Main features
- Multi-AZ failover: Decrease failover rate beside solely using Multi-AZ deployment.
Configuration
Enhanced Monitoring: monitor how the different processes or threads on a DB instance use the CPU, including the percentage of the CPU bandwidth and total memory consumed by each process.
Amazon Aurora
A cluster of DB instances
Main features
- Provide “Connection” mechanism:
- Each connection is handled by a specific DB instance
- When connecting to an Aurora cluster, the host name and port that you specify point to an intermediate handler called an “endpoint” => Abstract these connections
- Advantages:
- Don’t have to hardcode hostnames or write logic for load-balancing and rerouting connections when DB instances aren’t available.
- Different instances or groups perform different roles: Heavy-workload tasks will be redirected to high-capacity endpoints and vice versa.
Configuration
Parallel Query: enables Amazon Aurora to distribute the computational load of a single query across thousands of CPUs in Aurora’s storage layer
ElastiCache
Configuration
- Encryption at rest: Encrypt stored data in DB.
- Encryption in transit: Encrypt transfered data, sent command, delivered metadata, …
- AUTH default user access: Enable redis AUTH to authenticate with database when executing commands. Only enable through command.
Machine Learning
Amazon Comprehend
Main Features
- Determine the sentiment of a document
- A fully managed artificial intelligence (AI) service
Example
- Determine the sentiments of comments on a blog posting or a transcribed call to determine if your users loved or hated your content
Amazon Translate
Main Features
- Translate non-english texts into English
- A fully managed artificial intelligence (AI) service
Amazon Transcribe
Main Features
- Convert audio recordings into text
- A fully managed artificial intelligence (AI) service
Amazon Rekognition
Main Features
- Recognize images
- A fully managed artificial intelligence (AI) service
Example
- Determine nudity, sensitiveness, … of an image
- Category animal’s breeds, genders, type, …
Amazon Lex
Main Features
- A fully managed artificial intelligence (AI) service
- Using natural language models that can help you design, build, test, and deploy conversational interfaces or chatbots
Amazon Kendra
Main Features
- A fully managed artificial intelligence (AI) service
- Highly accurate and easy-to-use enterprise search service for all unstructured data that you store in AWS
Amazon Detective
Main Features
- A fully managed artificial intelligence (AI) service
- A security service that analyzes and visualizes security data to rapidly get to the root cause of your potential security issues.
Amazon SageMaker
Main Features
- A platform like Google Colab
- Allow you to freely build your customized models
- Use AWS built model to be used or further enhanced
Management & Governance
Service Quotas
Operations
Increase Quotas
- Submit form for increasing quotas number for specific configuration to AWS.
- Wait for approve and observe the new changed quotas
Networking & Content Delivery
API Gateway
Main features
- Throttling at multiple levels including global and by service call
- Add caching to API calls by provisioning an Amazon API Gateway cache and specifying its size in gigabytes.
CloudFront
Main features
- Caching static files (images, HTML, CSS, Javascript, …), front-end content website.
- Caching response contents for a request
- Integrate Lambda@Edge to handle 4 type of requests:
- After CloudFront receives a request from a viewer (viewer request)
- Before CloudFront forwards the request to the origin (origin request)
- After CloudFront receives the response from the origin (origin response)
- Before CloudFront forwards the response to the viewer (viewer response)
HTTP 504 (Gateway Timeout) errors from CloudFront mean that CloudFront didn’t get a timely response from your origin. General reason: origin takes long time to process request/response:
- Data base query slow
- Backend processes not efficiently
- Large data
- …
AWS Global Accelerator
Main features
- Suitable for non-HTTP use cases, such as gaming (UDP), IoT (MQTT), or Voice over IP, as well as for HTTP use cases that specifically require static IP addresses or deterministic, fast regional failover
VPC
AWS Network Firewall
Main features
- Supports domain name stateful network traffic inspection -> Create
AllowandDenylists with domain names. - NOT AN INTEGRATION SERVICES to any other resources like ELB, API Gateway, …
- A feature that exists in VPC, created as a resource separately in VPC, requires route table to route traffic through it if we need to apply network policies.
Security, Identity, & Compliance
AWS WAF
Configuration
Regular rule: Match condition only
Rate-based rule: Match condition & apply throttling
Storage
Simple Storage Service (S3)
Main Features
Fast-up data transfer:
- Enable Transfer Acceleration in the destination bucket
- Upload the collected data using Multipart Upload.
Configuration
Object Lock
- Enable/Disable to lock on “Objects”
With Bucket Versioning enabled, bucket are controlled with more features:
Default retention mode:
- Governance:
- Can’t overwrite or delete an object version or alter its settings unless having special permissions.
- To override or remove this settings, the TWO following conditions MUST BE SATISFIED:
- Must have the
s3:BypassGovernanceRetentionpermission - include
x-amz-bypass-governance-retention:trueas a request header with any request that requires overriding governance mode.
- Must have the
- Compliance:
- Can’t overwrite or delete an object version or alter its settings, including the root user in your AWS account.
- For compliance purpose in a specific duration.
In compliance mode, a protected object version can’t be overwritten or deleted by any user, including the root user in your AWS account. When an object is locked in compliance mode, its retention mode can’t be changed, and its retention period can’t be shortened. Compliance mode helps ensure that an object version can’t be overwritten or deleted for the duration of the retention period.
To override or remove governance-mode settings
Object Lock legal hold:
- Apply for “Objects”.
- Like “retention period”, prevent object from being deleted or overwritten.
Elastic Filesystem Storage (EFS)
Configuration
- EFS lifecycle policies: maximum days is only up to 365 days
Elastic Block Storage (EBS)
Main Features
- Snapshots are stored in S3 bucket.
Configuration
Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager (Amazon DLM): define policies that govern the lifecycle of these snapshots, ensuring regular backups are created and obsolete snapshots are automatically removed.
Amazon Storage Gateway
Main Features
- Used for creating a backup of data from your on-premises
- Providing low-latency access to data by caching frequently accessed data on-premises
AWS DataSync
Main Features
- Makes it simple and fast to move large amounts of data online between on-premises storage and Amazon S3, Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS), or Amazon FSx for Windows File Server
AWS Backup
Main Features
- Retention policy up to unlimited days. Automated backup for RDS Database supports the maximum of 35 days for retention policy
- Cross-account backup